Functions
Table of contents
- Table of contents
- What are functions?
- Use case: Native external references
- Use case: Custom external references
- Use case: App Events
- Use case: App Actions
- Working with functions
- Limitations
- Using the CMA
- Feedback
What are functions?
Functions are serverless workloads that run on the Contentful infrastructure to provide enhanced flexibility and customization. You can use functions to:
- connect to external systems and enrich the response of requests issued through Contentful's GraphQL API,
- filter, transform, and handle events coming from Contentful without having to set up your own server, or
- easily add a backend component to your app that can process actions triggered by the frontend, the CMA, or even by other apps.
Function workloads are executed in a sandboxed runtime environment. For more information, see the function limitations section.
Use case: Native external references
The Native external references feature allows you to seamlessly integrate content from external sources directly within your content model. By leveraging existing reference fields in the content model and the App Framework, you can link to third-party systems and pull content directly into Contentful without the need to create a custom frontend app.
Native external references use the standardized ResourceLink object entity to store references in a standard format which is native to the Contentful platform.
Native external references example
Examples showcase full functionality of Native external references.
| Function Example | Command | Description |
|---|---|---|
| native-external-references-mockshop | npx create-contentful-app@latest--example native-external-references-mockshop |
This function example uses Mock Shop API which is a fake e-commerce platform built by Shopify. You can also follow our tutorial for this example. |
The function event handler can parse 4 native external reference specific types of events:
- resources.search – retrieval of specific content based on search queries.
- resources.lookup - retrieval of specific content based on URNs (IDs).
- graphql.resourcetype.mapping - retrieval of resource type mappings, which determines what fields map to an external type.
- graphql.query - handles requests for resolving external data from GraphQL queries for the third-party API including introspection queries.
Each field that is configured with functions must map to a schema. We need to know the relation with the field and the corresponding GraphQL type in the function. Therefore, the field mapping response should include a field mapping for each field.
Given the schema below:
type Query {
product(id: String!): Product
}
type Product {
title: String!
description: String
inStock: Int!
}Here is the typing for GraphQLResourceTypeMapping:
type GraphQLResourceTypeMapping = {
resourceTypeId: string;
graphQLOutputType: string;
graphQLQueryField: string;
graphQLQueryArguments: Record<string, string>;
};GraphQLResourceTypeMapping would have the following values for the product field:
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
resourceTypeId: 'MockShop:Product' |
Resource Provider (a third-party system) combined with Resource Type (a specific type from the third-party system). |
graphQLQueryField: 'product' |
Field name in the query object of the given GraphQL schema. |
graphQLOutputType: 'Product' |
The external GraphQL type from the third-party API. |
graphQLQueryArguments: { id: '/urn' } |
Arguments that match for the field. id matches the argument for the product field. If left empty, an error for invalid arguments is returned. |
To get the schema, we run an introspection query that ends up triggering the graphql.query event. Note that this might happen repeatedly, and not when you install an app.
Use case: Custom external references
At times, you may need to reference content stored outside of Contentful. With Custom external references you can seamlessly integrate your custom code within the delivery context. Some of our marketplace apps, such as Shopify, Commercetools and Cloudinary, already have out-of-the-box support for this feature. For more information, see the Custom external references page.
Custom external references examples
Examples showcase full functionality of Custom external references.
| Function Example | Command | Description |
|---|---|---|
| function-mock-shop | npx create-contentful-app@latest--example function-mock-shop |
This function example uses Mock Shop API which is a fake e-commerce platform built by Shopify. You can also follow the our tutorial for this example. |
| function-potterdb | npx create-contentful-app@latest--examplefunction-potterdb |
This example serves as a function for Contentful. It is designed to proxy GraphQL requests to PotterDB. |
| function-potterdb-rest-api | npx create-contentful-app@latest--example function-potterdb-rest-api |
This example also serves as a function but is specifically tailored for wrapping a REST API in a GraphQL response. It's useful when you have a RESTful service, and you want to provide a GraphQL interface for it in your function. |
The following diagram displays the function request flow:
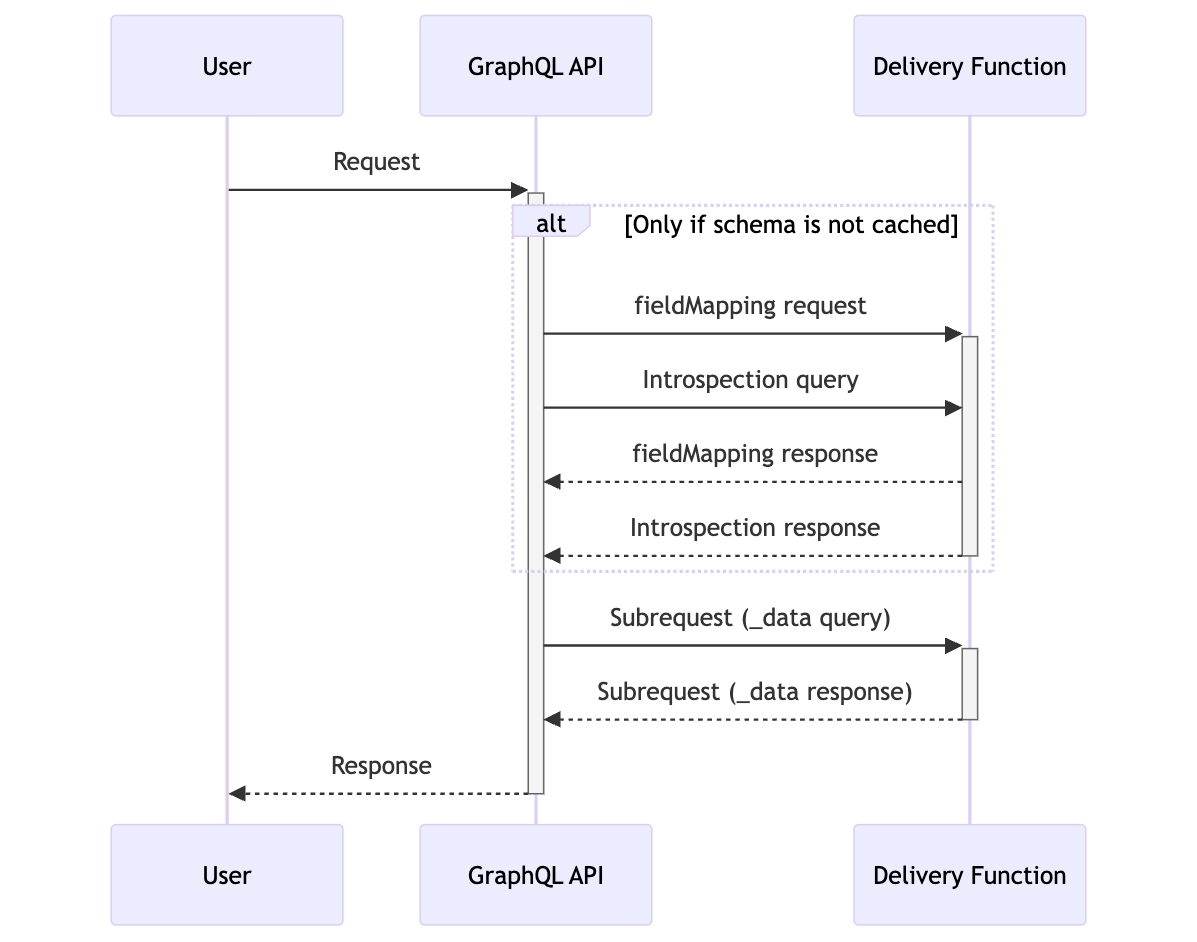
The function event handler can parse two different types of events:
- GraphQL field mapping event – the information returned by your function for this event is used to decide which GraphQL type is exposed on the additional
_datafield. - GraphQL query event - your function will receive this event whenever we want to get data for a GraphQL request. This includes introspection queries.
The function event handler can return two different types of responses:
Each field that is configured with functions, must map to a schema. We need to know the relation with the field and the corresponding GraphQL type in the function. Therefore, the field mapping response should include a field mapping for each field.
Given the schema below:
type Query {
product(id: String!): Product
}
type Product {
title: String!
description: String
inStock: Int!
}Here is the typing for GraphQLFieldMapping:
type GraphQLFieldTypeMapping = {
contentTypeId: string;
fieldId: string;
graphQLOutputType: string;
graphQLQueryField: string;
graphQLQueryArguments: Record<string, string>;
};GraphQLFieldTypeMapping would have the following values for the product field:
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
contentTypeId: 'Shop' |
Content type ID that includes the field with Resolve content on delivery checkbox enabled. |
fieldId: 'product' |
Field ID that includes the field with Resolve content on delivery checkbox enabled. |
graphQLQueryField: 'product' |
Field name in the query object of the given GraphQL schema. |
graphQLOutputType: 'Product' |
The GraphQL type that you want to attach to our _data field. |
graphQLQueryArguments: { id: '' } |
Arguments that match for the field. id matches the argument for the product field and the empty value states that the data from the field should be passed as is. |
The information coming in the event.fields array in the field mapping event is driven by the annotations that are added to the field once you enable Resolve content on delivery checkbox.
To get the schema, we run an introspection query that ends up triggering the graphql.query event. Note that this might happen repeatedly, and not when you install an app.
Custom external references templates
Templates allow developers to quickly scaffold an app with custom external references functions. These templates provide a starting point with skeleton code -- you must add your custom logic to meet your specific use case.
| Function Template | Command | Description |
|---|---|---|
| external-references | npx create-contentful-app@latest my-app --function external-references |
This template provides basic code to get started with custom external references. |
Use case: App Events
Subscribing to App Events unlocks powerful hooks into the content lifecycle, but it requires setting up and hosting a backend app. Using functions with App Events, developers gain access to a fully managed, scalable, and resilient serverless workflow that eliminates the need for custom backend infrastructure.
Functions streamline interaction with App Events, simplifying the process for developers. They can be used to:
- orchestrate intricate workflows across various services.
- perform resolution and hydration of data from external systems.
- implement custom logic to manage event-triggered builds or cache invalidation.
The following App Event functions are supported:
- Filter functions that run before any other processing, and are used to determine whether events are triggered or discarded.
- Transformation functions that run before request signing, and are used to modify the headers and body of the request.
- Handler functions that can be used as the target of the event, as opposed to targeting a URL.
All three function types receive the same headers and body as a traditional App Event.
App Event function examples
Examples showcase full functionality of App Event functions.
| Function Example | Command | Description |
|---|---|---|
| function-appevent-filter | npx create-contentful-app@latest my-app--example function-appevent-filter |
This example showcases how functions can be used to select which App Events are triggered. |
| function-appevent-transformation | npx create-contentful-app@latest my-app--example function-appevent-transformation |
This example portrays how a function can enrich the App Event request body with information from an external system. |
| function-appevent-handler | npx create-contentful-app@latest my-app--example function-appevent-handler |
This example exhibits proxying an App Event out to multiple external services. |
| function-comment-bot | npx create-contentful-app@latest my-app--example function-comment-bot |
This example highlights how functions can be used to make CMA requests using an App Identity. |
| autotagger | npx create-contentful-app@latest my-app--example autotagger |
This example uses a handler function alongside Private Installation Parameters to outline the skeleton for a configurable app that auto-tags entries of selected content types. |
App Event function templates
Templates allow developers to quickly scaffold an app with App Event functions. These templates provide a starting point with skeleton code -- you must add your custom logic to meet your specific use case.
| Function Template | Command | Description |
|---|---|---|
| appevent-filter | npx create-contentful-app@latest my-app --function appevent-filter |
App Event Filter functions enable you to decide which events your app should process by inspecting event payloads before they reach your main logic. |
| appevent-handler | npx create-contentful-app@latest my-app --function appevent-handler |
App Event Handler functions enable you to react to events in your Contentful space by executing custom code when specific events occur. |
| appevent-transformation | npx create-contentful-app@latest my-app --function appevent-transformation |
App Event Transformation functions enable you to modify event payloads before they reach their destination by adding, removing, or changing data in the event. |
| kitchen-sink | npx create-contentful-app@latest my-app --function kitchen-sink |
This unified template provides a single function that can handle all Contentful Management function types: App Action, App Event Handler, App Event Filter, and App Event Transformation. This approach allows you to manage multiple function types in a single codebase with shared logic. |
Use case: App Actions
Functions can be linked to and then invoked via App Actions, which provides apps an easy way to expose generic capabilities to their own frontends as well as to other apps.
Similar to App Event functions, App Action functions receive the same headers and body as a traditional App Action.
App Action function examples
Examples showcase full functionality of App Action functions.
| Function Example | Command | Description |
|---|---|---|
| function-appaction | npx create-contentful-app@latest my-app--example function-appaction |
This example contains a simple App Action function accompanied by a frontend Page location, highlighting how to link a function to an App Action and trigger it. |
App Action function templates
Templates allow developers to quickly scaffold an app with App Action functions. These templates provide a starting point with skeleton code -- you must add your custom logic to meet your specific use case.
| Function Template | Command | Description |
|---|---|---|
| appaction-call | npx create-contentful-app@latest my-app --function appaction-call |
App Action functions enable communication between apps by providing serverless endpoints that can be invoked through app actions. |
| kitchen-sink | npx create-contentful-app@latest my-app --function kitchen-sink |
This unified template provides a single function that can handle all Contentful Management function types: App Action, App Event Handler, App Event Filter, and App Event Transformation. This approach allows you to manage multiple function types in a single codebase with shared logic. |
Working with functions
This document provides an overview of functions, their use cases, and their limitations. Review the working with functions guide to dive deeper on creating, managing, and troubleshooting functions. There are also tutorials on Custom external references and Native external references for those specific use cases.
Limitations
Function executions per month and organization are subject to use in accordance with our current Technical Limits and Usage Limits. Additional considerations for developers utilizing functions are listed below.
Functions platform:
- Custom external references run only for uncached requests.
- Custom external references can only be used with short Text or JSON object field types.
- Custom external references allow you to integrate with external GraphQL APIs. You can also integrate with external REST APIs, but you have to provide your own GraphQL server implementation. For more information on the REST API implementation, see our PotterDB for REST example.
- Functions that resolve data in the delivery context are not currently compatible with live updates when using live preview.
Functions execution environment:
- Function code does not have access to the filesystem.
- Functions can handle event payloads less than 32MB in size.
- Requests to and responses from the provided CMA client must be less than 32MB in size. Utilize a
ReadableStreamif uploading an asset that exceeds this size, or instantiate your own client as described in the Using the CMA section below. - Functions have limited CPU and Memory resources available. Exceeding these resources will terminate the function.
Node.js compatibility:
Contentful Functions run in an environment which provides compatibility with many Node.js APIs but differs from the standard Node.js runtime. This means that while many npm packages will work, some relying on specific Node.js APIs might not function as expected. The following table outlines the support status for various Node.js APIs within the Functions runtime:
| API name | Support status in Functions runtime |
|---|---|
Assertion testing (assert) |
Supported |
Asynchronous context tracking (async_hooks) |
Supported |
Buffer (buffer) |
Supported |
| Console | Supported |
Crypto (crypto) |
Supported |
| Debugger | Not Supported |
Diagnostics Channel (diagnostics_channel) |
Supported |
DNS (dns) |
Supported |
| Errors | Supported |
Events (events) |
Supported |
File system (fs) |
Not supported |
| Globals | Supported |
HTTP (http) |
Not supported |
HTTP/2 (http2) |
Not supported |
HTTPS (https) |
Not supported |
| Inspector | Not supported |
Net (net) |
Supported |
OS (os) |
Not supported |
Path (path) |
Supported |
Performance hooks (perf_hooks) |
Partially supported |
Process (process) |
Supported |
Query strings (querystring) |
Supported |
Stream (stream) |
Supported |
String decoder (string_decoder) |
Supported |
Timers (timers) |
Supported |
TLS/SSL (tls) |
Partially supported |
UDP/datagram (dgram) |
Not supported |
URL (url) |
Supported |
Utilities (util) |
Supported |
| Web Crypto API | Supported |
| Web Streams API | Supported |
Zlib (zlib) |
Supported |
Using the CMA
The FunctionEventContext passed into App Event and App Action function invocations contains the information required to instantiate a contentful-management.js client. This simplifies the execution of CMA requests within the function on behalf of the App Identity.
To use the CMA, install contentful-management into your project and initialize it like so:
import * as contentful from "contentful-management";
export const handler: FunctionEventHandler<
FunctionTypeEnum.AppEventHandler,
> = async (event: AppEventRequest, context: FunctionEventContext) => {
const cma = contentful.createClient(
context.cmaClientOptions,
{
defaults: {
spaceId: context.spaceId,
environmentId: context.environmentId,
},
type: "plain",
}
);
// ...
}A preconfigured plain client is also provided in the context for convenience, but it is limited to requests and responses <1MB.
Feedback
Functions are continuously evolving to better meet your needs. We'd love to hear about your experience using functions and the use cases you're looking to implement.
To share your feedback, follow this this link.
